Home
Designs
Physics
Chemistry
Mathematics
Testing
Gallery
About Us
Seebeck Effect Simulator
The Mathematics Behind Our Flashlight
Modelling The Seebeck Effect Mathematically
V = αΔT
- Where V is the voltage
- Where α is the Seebeck coefficient (Different Metals Have Different Coefficients!)
- Where ΔT is the difference in temperature between the hot and cool ends of the two junctions
The Seebeck Coefficient
It is the amount of voltage produced between the two conductors when the temperature across them is sustained at 1 Kelvin (K).
Calculating Temperature Differences
V = a*(theta) + 1/2*b*(theta)^2
- Where V is the voltage.
- Where a and b are the seebeck coefficients which depend on the nature of the material.
- Where theta is the temperature difference between the two junctions.
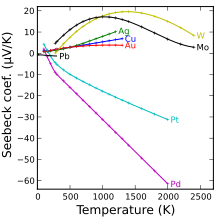
Figure 1: Metals and Their Seebeck Coefficient
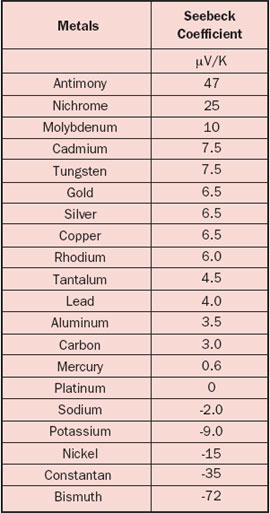
Figure 2: Modelling The Coefficients Mathematically